F5考试在即,相信各位备战的同学们都在如火如荼地翻书刷题模拟考,忙得不亦乐乎,如果你已晕眩在题海中,下面就来梳理一下重点内容。
正所谓知己知彼,方能百战百胜,那么首先,就要了解考试题型及覆盖的考纲内容,来开展高效的备考计划。
5科目考试由三个Section组成:Section A+Section B+Section C
Section A:由15道客观题构成,每题2分,总共30分,考点覆盖全部知识点;
Section B:由三个情景分析案例构成,各个情景分析案例包含5道客观题,每题2分,总共30分,考点覆盖全部知识点;
Section C:由两道20分的大题构成,考点出自PartB Decision-making techniques,Part C Budgeting and control,Part D Performance measurement and control。
你的复习内容真的全面覆盖了吗?!看一下重点大盘点:(排名分了先先先后噢!)
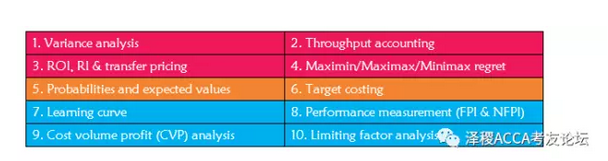
如果发现还没复习到的知识点,就先速速浏览一下历年考点分布吧!记得看完做练习哟!
重要考点分析:
1.Variance analysis
历年考题练习:
2016 Specimen–Section A–Q5
2016 Specimen–Section C–Q31
2016 Sep–Section A–Q3/7/12
2016 Sep–Section B–Q23
2016 Mar/June–Section B–Q5
2015 Sep/Dec–Section B–Q3
2015 June–Section A–Q14/15/18
2015 June–Section B–Q3
2014 Dec-Section B-Q5
2014 June–Q5
2013 Dec-Q5
2013 June–Q4
Variance analysis是F5科目较重要的考点,沿袭F2 Basic variance基础上,F5进一步加深分析了Planning variance and operational variance,Materials mix and yield variances,Sales mix and quantity variances,其计算方法及差异比较应深入掌握。
2.Throughput accounting
历年考题练习:
2016–Specimen–Section A–Q13
2016–Specimen–Section B–Q17/18/20
2016–Sep–Section A-Q11
2015–June–Section A–Q9/Q20
2014–Dec–Section B–Q2
2013 Dec-Q2
历年考题分析1:2013 Dec-Q2
该题是典型Throughput accounting计算题型,需注意的是正确掌握计算方法及公式:Throughput accounting ratio=throughput return per factory hour/cost per factory hour.当多产品比较时,需计算各产品TA Ratio进行排序。
历年考题分析2:2015 June–Section A–Q20
该题型考核对Throughput accounting概念的掌握和理解。Throughput accounting有三个基本概念:1.Material cost是相关费用,其他费用包括labor cost均作为fixed costs归集处理,即Sales–material cost=Throughput,Throughput–fixed cost=Profit;2.以JIT环境为理论基础,存货不能创造价值,理想的存货水平为0;3.“Making money means maximizing throughput.”最大化throughput,即最大化盈利。
3.ROI,RI&transfer pricing
Transfer pricing
历年考题练习:
2016 Specimen–Section A–Q14
2016 Mar/June–Section B–Q4
2015 June-Section B-Q2
2014 Dec–Section A–Q8
2014 June–Q3
2013 Dec–Q1
历年考题分析1:2015 June-Section B-Q2
该题全面考核了transfer pricing核心知识点,包括Minimum transfer price,Maximum transfer price,以及transfer price对企业整体的作用和影响。需注意对于供应部门(卖方)最低可提供价格是边际成本+机会成本,一般考生都会忽略计算机会成本,应掌握机会成本的识别。对于购买部门,愿意接受的最大价格是同等产品最低市场价格,以及扣减内部包装运输所节省的费用。
计算方法:
Minimum transfer price:=Marginal cost+Opportunity cost
(Supplying department lowest acceptable limit)
Maximum transfer price:=lowest market price-internal cost savings in packaging and delivery
(Receiving department highest acceptable limit)
ROI(Return on investment)=(Profit/Capital employed)100%.
历年考题练习:
2016 Sep-Section A–Q10
2015 Sep/Dec–Section B–Q5
2015 June–Section A–Q19
RI(Residual income)=Profit-notional or imputed interest cost
历年考题练习:
2015 June-Section A–Q1
2014 Dec–Section A–Q1
4.Maximin/Maximax/Minimax regret decision rule
历年考题练习:
2016 Sep–Section B–Q16/17
2015 June–Section A–Q4
2008 Dec Q2
Maximin
The'play it safe'basis for decision-making is referred to as the maximin basis.This is short for
'maximise the minimum achievable profit'.
Maximax
A basis for making decisions by looking for the best outcome is known as the maximax basis,short for'maximise the maximum achievable profit'.
Minimax regret
The'opportunity loss'basis for decision-making is known as minimax regret.
The minimax regret rule aims to minimise the regret from making the wrong decision.Regret is the opportunity lost through making the wrong decision.
5.Probabilities and expected values
历年考题练习:
2016 Dec–CBE–Q14
2014 Dec–Section A–Q17
2014 June Q4
An expected value is a weighted average value of the different possible outcomes from a decision,where weightings are based on the probability of each possible outcome.
Expected values are used to support a risk-neutral attitude.Expected values are more valuable as a guide to decision-making where they refer to outcomes which will occur many times over.
6.Target costing
历年考题:
2016 Specimen–Section A-Q2
2016 Sep–Section A–Q7
2016 Sep–Section B–Q26-30
2015 Sep/Dec–Section B–Q1
2015 June–Section A–Q3
2014 Dec–Section A–Q15
历年考题分析1:2014 Dec–Section A–Q15
掌握Target costing计算的要素及步骤:
Step 1 Estimate sales volume
Step 2 Decide a target selling price
Step 3 Estimate the required profit
Step 4 Calculate:Target cost=Target selling price–Target profit
Step 5 Prepare an estimated cost for the product
Step 6 Calculate:Target cost gap=Estimated cost–Target cost.
Step 7 Make efforts to close the gap.
7.Learning curve
历年考题练习:
2016 Specimen–Section B–Q21/22/23
2016–Sep–Section B-Q29
2015–June–Section A-Q16
2015 June-Section B-Q3
2014 Dec-Section B–Q1
2013–Dec–Q3
历年考题分析1:2015 June-Section B-Q3
该题是learning curve和variance analysis两个重要知识点的结合运用。
历年考题分析2:2014 Dec-Section B–Q1
该题需注意的是计算price for new seat,即incremental time for 8th unit,即根据公式Learning curve formula=y=axb,Y=12*8–•415=5•0628948 hours,该值是累计制造8个均摊至每一个的平均用时,非第八个新增用时。因此,要计算出制造第八个的增量用时,应将累计制造8个总用时减去累计制造7个总用时,才是第八个的增量用时。
即,累计7个平均用时Y=12*7–•415=5•3513771 hours
累计8个平均用时Y=12*8–•415=5•0628948 hours
累计7个总用时=5•3513771 hours*7 units=37•45964 hours.
累计8个总用时=5•0628948 hours*8 units=40•503158 hours
第八个增量用时=40•503158 hours-37•45964 hours=3•043518 hours
8.Performance measurement
Financial performance indicators(FPIs)
a)Profit(both gross profit and net profit)
b)Revenue
c)Costs
d)Cash flows
e)Debt and gearing
Non-financial performance indicators(NFPIs)
a)Quality
b)Speed or efficiency
c)Delivery
d)Reliability
e)Customer satisfaction
f)Innovation
历年考题练习:
2016 Specimen–Section C–Q32
2016 Sep-Section C–Q31
2015 June–Section A–Q13
2014 June–Q3
2013 Dec–Q4
较易在Section C大题中考核,掌握并分析财务及非财务指标,结合案例进行分析。
9.Cost volume profit(CVP)analysis
历年考题练习:
2016 Sep–Section B–Q20
2016–Mar/June–Section B–Q2
2015 Sep/Dec–Section B–Q4
掌握多产品Weighted average C/S ratio计算。
相关公式:
Margin of safety=budgeted sales–breakeven sales
Breakeven sales revenue=fixed costs/weighted average C/S ratio
10.Limiting factor analysis
历年考题分析:
2016 Specimen–Section A–Q8/20
2016 Sep–Section A–Q9
2016 Sep–Section C–Q32
2014 June–Q2
Slack occurs when maximum availability of a resource is not used:slack is the amount of the unused resource or other constraint,where the constraint is a'less than or equal to'constraint.
Surplus occurs when more than a minimum requirement is used:surplus is the excess over the
minimum amount of constraint,where the constraint is a'more than or equal to'constraint.
最新出炉,小试牛刀
刚结束的2017 March exam中,Section A考核了ROI和RI的辨析题,快来开动大脑挑战一下最新题型:
A company has two divisions.The divisions are identical in terms of the number and type of machines they have and the operations they carry out.However,one division was set up four years ago and the other was set up one year ago.Head office appraises the division using both return on investment(ROI)and residual income(RI).
Which of the following statements is correct in relation to the outcome of the appraisal for each division?
A.Both ROI and RI will favour the older division
B.ROI will favour the older division,but RI will treat each fairly
C.RI will favour the newer division and ROI will favour the older division
D.Both RI and ROI will favour the newer division
这道题的考点是什么?
ROI及RI在divisional performance appraisal中的运用及其利弊。
这道题的答案是什么?
正确答案选A
大家都选对了吗?下面是详细说明:
计算ROI:(divisional profit/capital employed)x 100%
计算RI:divisional profit–(capital employed x cost of capital)
要了解ROI和RI如何在每个部门中运用,要公允假设他们都产生相同的profit(实际相同)。两个部门都有相同的assets-然而,老部门将受到更多的depreciation,由于多消耗3年的depreciation,导致降低了capital employed。
看这两个部门的计算,与新部门相比,较小的capital employed将给老部门虚高的ROI。
同样,老部门的“imputed interest”(capital employed x cost of capital)也更小。
两个部门都使用公司总体的cost of capital,从而使老部门比新部门RI更高。
如果对这类题目有疑惑,可以代入一些数字来分析。如果两个部门都赚了10万美元的profits,但是老部门assets’net book value是50万美元,而新部门assets’net book value为200万美元(for example),相应得到的ROI为20%和5%。同样,如果您使用cost of capital是10%,相应两个部门RI是5万美元和损失10万美元——显然,ROI和RI都有利于老部门。
最后,记得结合重点梳理知识点,对于错题要勤加练习!!祝大家考出好成绩!
版权声明:本文为泽稷网校ACCA研究院独家原创稿件 未经授权,禁止转载
点击在线咨询泽稷老师,ACCA中文宝典免费领,更有机会获得海量免费ACCA学习资料。





 白金级认可培训资质(总部)
白金级认可培训资质(总部)
 课程试听
课程试听
 职业规划
职业规划
 ACCA中文教材
ACCA中文教材
 考位预约
考位预约
 免费资料
免费资料




 题库下载
题库下载
 模拟机考
模拟机考




 CFA®成绩查询
CFA®成绩查询




 GARP协会官方认可FRM®备考机构
GARP协会官方认可FRM®备考机构





















